Drug addiction has become quite common among the youth in the USA and is turning out to be a major issue. Drugs like cocaine, heroin and various opiates are widely taken by the youngsters for the sensations of euphoria and heightened self-confidence.
Around 35.3 million Americans ages 12 and older reported to having used cocaine in the year 2006.
Cocaine is a powerfully addictive stimulant that can have a variety of adverse effects on the body and mind. The drug usually appears in powdered form and is cut with various fillers like baking soda and local anesthetics to increase its weight. Cocaine can also be cut with other drugs such as methamphetamine.
Regardless of the method of administration there are high chances of the individuals taking an overdose of the drug which can result in cardiac arrest or seizures followed by respiratory arrest. Drug addiction treatment is crucial at this point.

Cocaine Addiction
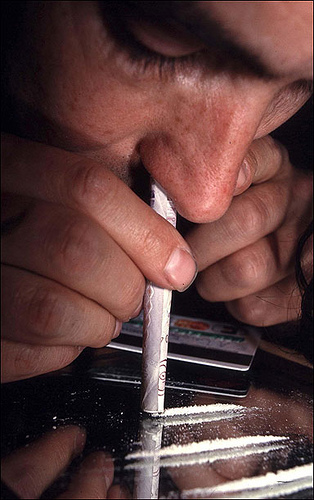
Most Common Method of Cocaine Administration
- snorting
- injecting
- smoking
- swallowing
- chewing it in leaf form
Effects of cocaine can last from 20 minutes to a few hours depending on the dosage and purity of the drug.
As soon as a person takes cocaine, hyperactivity, increased blood pressure & heart rate, restlessness and euphoria are experienced. What causes addiction is that the euphoria is often followed by feelings of depression and an intense craving to experience the euphoria again. However, there are numerous side effects related with using cocaine starting from paranoia to impotence, which increase with frequent usage.
Some people even suffer hallucinations, and paranoid delusions with prolonged use. Cocaine can also cause greater heat production resulting in hyperthermia, which can lead to muscle cell destruction and renal failure.
Long Term Effects of Cocaine Use
- deviated septum
- gingivitis
- kidney disease
- renal failure
Proper care and scientifically proven treatments can help an addict lead a cocaine-free life. Most experts agree that the facility where one seeks treatment itself plays a very important role in recovery.